Donkey Kong (video game)
| Donkey Kong | |
|---|---|
 A 1:2 scale replica Donkey Kong arcade cabinet |
|
| Developer(s) | Nintendo |
| Publisher(s) | Nintendo |
| Designer(s) | Shigeru Miyamoto |
| Composer(s) | Yukio Kaneoka[1] |
| Series | Mario, Donkey Kong |
| Platform(s) | Arcade |
| Release date(s) | Arcade
Virtual Console
|
| Genre(s) | Platform |
| Mode(s) | Single-player, multiplayer |
| Rating(s) |
|
| Cabinet | Upright, mini and cocktail |
| Arcade system | Main CPU: Zilog Z80 (at 3.072 MHz) Sound CPU: I8035 (at 400 kHz) Sound chips: DAC (at 400 kHz), samples (at 400 kHz) Monitor: raster, standard resolution 224 × 256 (vertical), 256 palette colors |
Donkey Kong (ドンキーコング Donkī Kongu) is an arcade game developed by Nintendo, released in 1981. It is an early example of the platform genre, as the gameplay focuses on maneuvering the main character across a series of platforms while dodging and jumping over obstacles. In it, Jumpman (now known as Mario) must rescue a damsel in distress, Lady (now known as Pauline), from a giant ape named Donkey Kong. The hero and ape later became two of Nintendo's most popular characters.
The game was the latest in a series of efforts by Nintendo to break into the North American market. Hiroshi Yamauchi, Nintendo's president at the time, assigned the project to a first-time game designer named Shigeru Miyamoto. Drawing from a wide range of inspirations, including Popeye and King Kong, Miyamoto developed the scenario and designed the game alongside Nintendo's chief engineer, Gunpei Yokoi. The two men broke new ground by using graphics as a means of characterization, including cut scenes to advance the game's plot, and integrating multiple stages into the gameplay.
Despite initial misgivings on the part of Nintendo's American staff, Donkey Kong proved a success in North America and Japan. Nintendo licensed the game to Coleco, who developed home console versions for numerous platforms. Other companies cloned Nintendo's hit and avoided royalties altogether. Miyamoto's characters appeared on cereal boxes, television cartoons, and dozens of other places. A court suit brought on by Universal City Studios, alleging Donkey Kong violated their trademark of King Kong, ultimately failed. The success of Donkey Kong and Nintendo's win in the courtroom helped position the company to dominate the video game market in the 1980s and early 1990s.
Contents |
Gameplay

Donkey Kong is one of the earliest examples of the platform genre (it is sometimes said to be the first platform game, although it was preceded by Space Panic).[2] Competitive video gamers and referees stress the game's high level of difficulty compared to other classic arcade games. Winning the game requires patience and the ability to accurately time Jumpman's ascent.[3] In addition to presenting the goal of saving the Lady, the game also gives the player a score. Points are awarded for finishing screens; leaping over obstacles; destroying objects with a hammer power-up; collecting items such as hats, parasols, and purses (presumably belonging to the Lady/Pauline); and completing other tasks. The player typically receives three lives with a bonus awarded for the first 10,000 points,[4] although this can be modified via the game's built in DIP switches.
The game is divided into four different one-screen stages. Each represents 25 meters of the structure Donkey Kong has climbed, one stage being 25 meters higher than the previous. The final screen occurs at 100 m. Later ports of the game omit or change the sequence of the screens. The original arcade version includes:
- Screen 1 (25 m), Jumpman must scale a seven-story construction site made of crooked girders and ladders while jumping over or hammering barrels and oil barrels tossed by Donkey Kong. The hero must also avoid flaming balls, which generate when an oil barrel collides with an oil drum. Players routinely call this screen "Barrels".[5]
- Screen 2 (50 m), Jumpman must climb a five-story structure of conveyor belts, each of which transports cement pans. The fireballs also make another appearance. This screen is sometimes referred to as the "Factory" or "Pie Factory" due to the resemblance of the cement pans to pies.[5]
- Screen 3 (75 m), Jumpman rides up and down elevators while avoiding fireballs and bouncing objects, presumably spring weights. The bouncing weights (the hero's greatest danger in this screen) emerge on the top level and drop near the rightmost elevator. The screen's common name is "Elevators".[5] This screen appears as an unlockable stage in Super Smash Bros. Brawl.
- Screen 4 (100 m), Jumpman must remove the eight rivets which support Donkey Kong. The fireballs remain the primary obstacle. Removing the final rivet causes Donkey Kong to fall and the hero to be reunited with the Lady. This is the final screen of each level. Players refer to this screen as "Rivets".[5]
The player loses a life if:
- Jumpman runs into a barrel, fireball, flaming oil barrel, spring weight, cement pan, or Donkey Kong;
- Jumpman falls off the structure or through open rivet holes;
- The bonus timer reaches 0.
These screens combine to form levels, which become progressively tougher. For example, Donkey Kong begins to hurl barrels faster and sometimes diagonally, and fireballs get speedier. The victory music alternates between levels 1 and 2. The 22nd level is unofficially known as the kill screen, due to an error in the game's programming that kills Jumpman after a few seconds, effectively ending the game.[5] With its four unique levels, Donkey Kong was the most complex arcade game at the time of its release, and only the second game to feature multiple levels (the first was Gorf by Midway Games).[6]
Story and characters
The eponymous Donkey Kong is the game's de facto villain. He is the pet of a carpenter named "Jumpman" (a name chosen for its similarity to "Walkman" and "Pac-Man"; the character was later renamed Mario and made a plumber, rather than a carpenter, when Mario Bros. was released).[7] The carpenter mistreats the ape, so Donkey Kong escapes and kidnaps Jumpman's girlfriend, originally known as the Lady, but later named Pauline. The player must take the role of Jumpman and rescue the girl. This was the first occurrence of the damsel in distress scenario that would provide the template for countless video games to come.[3]
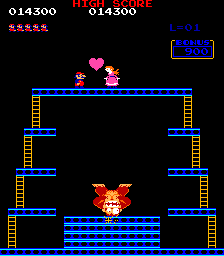
The game uses graphics and animation as vehicles of characterization. Donkey Kong smirks upon Jumpman's demise. The Lady is instantly recognized as female from her pink dress and long hair,[8] and "HELP!" appears frequently beside her. Jumpman, depicted in red overalls and cap, is an everyman character, a type common in Japan. Graphical limitations forced his design: Drawing a mouth was too difficult, so the character got a mustache ;[9] the programmers could not animate hair, so he got a cap; and to make his arm movements visible, he needed colored overalls.[10] The artwork used for the cabinets and promotional materials make these cartoon-like character designs even more explicit. The Lady/Pauline, for example, appears as a disheveled Fay Wray in a torn dress and stiletto heels.[8]
Donkey Kong is the first example of a complete narrative told in video game form, and it employs cut scenes to advance its plot. The game opens with the gorilla climbing a pair of ladders to the top of a construction site. He sets the Lady down and stamps his feet, causing the steel beams to change shape. He then moves to his final perch and sneers. This brief animation sets the scene and adds background to the gameplay, a first for video games. Upon reaching the end of the stage, another cut scene begins. A heart appears between Jumpman and the Lady, but Donkey Kong grabs the woman and climbs higher, causing the heart to break. The narrative concludes when Jumpman reaches the end of the rivet stage. He and the Lady are reunited, and a short intermission plays.[11] The game then starts over at a higher level of difficulty.
Development
As of the beginning of 1981, Nintendo's efforts to sell in the North American video game market had failed, culminating with the flop Radar Scope in 1980. To keep the company afloat, company president Hiroshi Yamauchi decided to convert unsold Radar Scope games into something new. He approached a young industrial designer named Shigeru Miyamoto, who had been working for Nintendo since 1977, to see if Miyamoto thought he could design an arcade game. Miyamoto said he could.[12] Yamauchi appointed Nintendo's head engineer, Gunpei Yokoi, to supervise the project.[13] Some sources also claim that Ikegami Tsushinki performed some of the development.[14][15][16]
At the time, Nintendo was pursuing a license to make a game based on the Popeye comic strip. When this fell through, Nintendo decided that it would take the opportunity to create new characters that could then be marketed and used in later games.[10] Miyamoto came up with many characters and plot concepts, but he eventually settled on a gorilla/carpenter/girlfriend love triangle that mirrored the rivalry between Bluto and Popeye for Olive Oyl.[7] Bluto became an ape, which Miyamoto said was "nothing too evil or repulsive". He would be the pet of the main character, "a funny, hang-loose kind of guy."[17] Miyamoto has also named "Beauty and the Beast" and the 1933 film King Kong as influences.[18] Although its origin as a comic strip license played a major part, Donkey Kong marked the first time that the storyline for a video game preceded the game's programming rather than simply being appended as an afterthought.[19] An unrelated Popeye game would eventually be released by Nintendo in 1982.
Yamauchi wanted to primarily target the North American market, so he mandated that the game be given an English title. Miyamoto decided to name the game for the ape, whom he felt to be the strongest character.[7] The story of how Miyamoto came up with the name "Donkey Kong" varies. A popular urban myth says that the name was originally meant to be "Monkey Kong", but was misspelled or misinterpreted due to a blurred fax or bad telephone connection.[20] Another story claims Miyamoto looked in a Japanese-English dictionary for something that would mean "stubborn gorilla,"[13] or that "Donkey" was meant to convey "silly" or "stubborn"; "Kong" was common Japanese slang for "gorilla".[10] A rival claim is that he worked with Nintendo's export manager to come up with the title, and that "Donkey" was meant to represent "stupid and goofy".[21]
Miyamoto had high hopes for his new project. He lacked the technical skills to program it himself, so instead came up with concepts and consulted technicians to see if they were possible. He wanted to make the characters different sizes, move in different manners and react in various ways. Yokoi thought Miyamoto's original design was too complex.[22] Another idea Yokoi suggested was to use see-saws to catapult the hero across the screen; this was too difficult to program. Miyamoto then thought of using sloped platforms, barrels and ladders. When he specified that the game would have multiple stages, the four-man programming team complained that he was essentially asking them to make the game repeatedly.[23] Nevertheless, they followed Miyamoto's design, creating about 20,000 lines of code.[24] Yukio Kaneoka composed a simplistic soundtrack to serve as background music for the levels and story events.[25][1]
Hiroshi Yamauchi thought the game was going to sell well and called Minoru Arakawa, head of Nintendo's operations in the U.S., to tell him. Nintendo's American distributors, Ron Judy and Al Stone, brought Arakawa to a lawyer named Howard Lincoln to secure a trademark.[26]

The game was sent to Nintendo of America for testing. The sales manager hated it for being too different from the maze and shooter games common at the time,[27] and Judy and Lincoln expressed reservations over the strange title. Still, Arakawa swore that it would be big.[26] American staffers asked Yamauchi to change the name, but he refused. Arakawa and the American staff began translating the storyline for the cabinet art and naming the other characters. They chose "Pauline" for the Lady, after Polly James, wife of Nintendo's Redmond, Washington, warehouse manager, Don James. Jumpman was eventually named for Mario Segale, the office landlord.[28] These character names were printed on the American cabinet art and used in promotional materials. Donkey Kong was ready for release.[29]
Stone and Judy convinced the managers of two bars in Seattle, Washington, to set up Donkey Kong machines. The managers initially showed reluctance, but when they saw sales of $30 a day—or 120 plays—for a week straight, they requested more units.[30] In their Redmond headquarters, a skeleton crew composed of Arakawa, his wife Yoko, James, Judy, Phillips and Stone set about gutting 2,000 surplus Radar Scope machines and converting them with Donkey Kong motherboards and power supplies from Japan.[31] The game officially went on sale in July 1981.[32]
In his 1982 book Video Invaders, Steve Bloom described Donkey Kong as "another bizarre cartoon game, courtesy of Japan".[33] Donkey Kong was, however, extremely popular in the United States and Canada. The game's initial 2,000 units sold, and more orders were made. Arakawa began manufacturing the electronic components in Redmond because waiting for shipments from Japan was taking too long.[34] By October, Donkey Kong was selling 4,000 units a month, and by late June 1982, Nintendo had sold 60,000 Donkey Kong games overall and earned $180 million.[32] Judy and Stone, who worked on straight commission, became millionaires.[34] Arakawa used Nintendo's profits to buy 27 acres (110,000 m2) of land in Redmond in July 1982.[35] The game made another $100 million in its second year of release.[36] It remained Nintendo's top seller into summer 1983.[37] Donkey Kong also sold steadily in Japan.[38]
Licensing and ports

By late June 1982, Donkey Kong's success had prompted more than 50 parties in the U.S. and Japan to license the game's characters.[39] Mario and his simian nemesis appeared on cereal boxes, board games, pajamas, and manga. In 1983, the animation studio Ruby-Spears produced a Donkey Kong cartoon (as well as Donkey Kong Jr) for the Saturday Supercade program on CBS. In the show, mystery crime-solving plots in the mode of Scooby-Doo are framed around the premise of Mario and Pauline chasing Donkey Kong, who has escaped from the circus. The show lasted two seasons.
Makers of video game consoles were also interested. Taito offered a considerable sum to buy all rights to Donkey Kong, but Nintendo turned them down.[31] Rivals Coleco and Atari approached Nintendo in Japan and the United States respectively. In the end, Yamauchi granted Coleco exclusive console and tabletop rights to Donkey Kong because he felt that "It [was] the hungriest company".[40] In addition, Arakawa felt that as a more established company in the U.S., Coleco could better handle marketing. In return, Nintendo would receive an undisclosed lump sum plus $1.40 per game cartridge sold and $1 per tabletop unit. On December 24, 1981, Howard Lincoln drafted the contract. He included language that Coleco would be held liable for anything on the game cartridge, an unusual clause for a licensing agreement.[41] Arakawa signed the document the next day, and, on February 1, 1982, Yamauchi persuaded the Coleco representative in Japan to sign without running the document by the company's lawyers.[42]
Coleco did not offer the game stand-alone; instead, they bundled it with their ColecoVision. The units went on sale in July 1982. Coleco's version was a more accurate port than earlier games that had been done. Six months later, Coleco offered Atari 2600 and Intellivision versions, too. Notably, they did not port it to the Atari 5200, a system comparable to their own (as opposed to the less powerful 2600 and Intellivision). Coleco's sales doubled to $500 million and their earnings quadrupled to $40 million.[43] Meanwhile, Atari got the license for computer versions of Donkey Kong and released it for the Atari 400/800. When Coleco unveiled the Adam Computer, running a port of Donkey Kong at the 1983 Consumer Electronics Show in Chicago, Illinois, Atari protested that it was in violation of the licensing agreement. Yamauchi demanded that Arnold Greenberg, Coleco's president, shelve his Adam port. This version of the game was cartridge-based, and thus not a violation of Nintendo's license with Atari; still, Greenberg complied. Ray Kassar of Atari was fired the next month, and the home PC version of Donkey Kong fell through.[44]
In 1983, Atari released several computer versions under the Atarisoft label. All of the computer ports had the cement factory level, while most of the console versions did not. None of the home versions of Donkey Kong had all of the intermissions or animations from the arcade game. Some have Donkey Kong on the left side of the screen in the barrel level (like he is in the arcade game) and others have him on the right side.

Miyamoto created a greatly simplified version for the Game & Watch multiscreen. Other ports include the Apple II, Atari 7800, Commodore 64, Commodore VIC-20, Famicom Disk System, PC, ZX Spectrum, Amstrad CPC and Mini-Arcade. The game was ported to the Family Computer in 1983 as one of the system's three launch titles; the same version was a launch title for the Famicom's North American version, the Nintendo Entertainment System. However, the cement factory level is not included, since Nintendo did not have large enough cartridge ROMs available in the beginning. At the title screen, this port includes a new song composed by Yukio Kaneoka;[1] an arrangement of the tune appears in Donkey Kong Country for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System. Both Donkey Kong and its sequel, Donkey Kong, Jr., are included in the 1988 NES compilation Donkey Kong Classics. The NES version was rereleased as an unlockable game in Animal Crossing for the GameCube and as an item for purchase on the Wii's Virtual Console. The original arcade version of the game appears in the Nintendo 64 game Donkey Kong 64. In 2004, Nintendo released the NES version for the Game Boy Advance Classic NES series and on the e-Reader.[45]
Clones
Other companies bypassed Nintendo completely. In 1981, O.R. Rissman, president of Tiger Electronics, obtained a license to use the name King Kong from Universal City Studios. Under this title, Tiger created a handheld game with a scenario and gameplay based directly on Nintendo's creation.[46] Crazy Kong is another example, a clone manufactured by Falcon and licensed for some non-American markets. Nevertheless, Crazy Kong machines found their way into some American arcades during the early 1980s, often installed in cabinets marked as Congorilla. Nintendo was quick to take legal action against those distributing the game in the U.S.[47] Bootleg copies of Donkey Kong also appeared in both North America and France under the Crazy Kong, Konkey Kong or Donkey King names.
In 1983, Sega created a Donkey Kong clone called Congo Bongo. Despite being in isometric perspective, the gameplay is very similar.
As with other popular arcade games at the time, there were also unofficial clones for home systems. Clones on the TRS-80 Color Computer include Donkey King and Monkey Kong. A Color Computer 3 version was created in 2007 by "translating" the original code to 6809 code. The result is a game that looks and feels just like the original, besides the aspect ratio of the screen. Other clones include Killer Gorilla (Micro Power), one of the best selling games on the BBC Micro and Acorn Electron.
Universal City Studios, Inc. v. Nintendo Co., Ltd.
Nintendo's success with Donkey Kong was not without obstacles. In April 1982, Sid Sheinberg, a seasoned lawyer and president of MCA and Universal City Studios, learned of the game's success and suspected it might be a trademark infringement of Universal's own King Kong.[32] On April 27, 1982, he met with Arnold Greenberg of Coleco and threatened to sue over Coleco's home version of Donkey Kong. Coleco agreed on May 3, 1982 to pay royalties to Universal of 3% of their Donkey Kong's net sale price, worth about $4.6 million.[48] Meanwhile, Sheinberg revoked Tiger's license to make its King Kong game, but O. R. Rissman refused to acknowledge Universal's claim to the trademark.[49] When Universal threatened Nintendo, Howard Lincoln and Nintendo refused to cave. In preparation for the court battle ahead, Universal agreed to allow Tiger to continue producing its King Kong game as long as they distinguished it from Donkey Kong.[39]
Universal officially sued Nintendo on June 29, 1982 and announced its license with Coleco. The company sent cease and desist letters to Nintendo's licensees, all of which agreed to pay royalties to Universal except Milton Bradley and Ralston Purina.[50]
Universal City Studios, Inc. v. Nintendo, Co., Ltd. was heard in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York by Judge Robert W. Sweet. Over seven days, Universal's counsel, the New York firm Townley & Updike, argued that the names King Kong and Donkey Kong were easily confused and that the plot of the game was an infringement on that of the films.[51] Nintendo's counsel, John Kirby, countered that Universal had themselves argued in a previous case that King Kong's scenario and characters were in the public domain. Judge Sweet ruled in Nintendo's favor, awarding the company Universal's profits from Tiger's game ($56,689.41), damages and attorney's fees.[52]
Universal appealed, trying to prove consumer confusion by presenting the results of a telephone survey and examples from print media where people had allegedly assumed a connection between the two Kongs.[53] On October 4, 1984, however, the court upheld the previous verdict.[54]
Nintendo and its licensees filed counterclaims against Universal. On May 20, 1985, Judge Sweet awarded Nintendo $1.8 million for legal fees, lost revenues, and other expenses.[55] However, he denied Nintendo's claim of damages from those licensees who had paid royalties to both Nintendo and Universal.[56] Both parties appealed this judgment, but the verdict was upheld on July 15, 1986.[57]
Nintendo thanked John Kirby with a $30,000 sailboat named Donkey Kong and "exclusive worldwide rights to use the name for sailboats".[58] The court battle also taught Nintendo they could compete with larger entertainment industry companies.[59]
Legacy
Donkey Kong spawned the sequels Donkey Kong Jr. and Donkey Kong 3, as well as the spin-off Mario Bros. A complete re-make of the original arcade game on the Game Boy, named Donkey Kong or Donkey Kong '94 contained levels from both the original Donkey Kong and Donkey Kong Jr arcades. It starts with the same damsel-in-distress premise and four basic locations as the arcade game and then progresses to 97 additional puzzle-based levels. It was the first game to have built-in enhancement for the Super Game Boy accessory. The arcade version makes an appearance in Donkey Kong 64 in the Frantic Factory level. Nintendo revived the Donkey Kong license in the 1990s for a series of platform games and spin-offs developed by Rare, beginning with Donkey Kong Country in 1994. In 2004, Nintendo released Mario vs. Donkey Kong, a sequel to the Game Boy title. In it, Mario must chase Donkey Kong to get back the stolen Mini-Mario toys. In the follow-up Mario vs. Donkey Kong 2: March of the Minis, Donkey Kong once again falls in love with Pauline and kidnaps her, and Mario uses the Mini-Mario toys to help him rescue her. Donkey Kong Racing for Gamecube was in development by Rare, but was canceled when Microsoft purchased the company. In 2004, Nintendo released the first of the Donkey Konga games, a rhythm-based game series that uses a special bongo controller. Donkey Kong Jungle Beat (2005) is a unique platform action game that uses the same bongo controller accessory. In 2007, Donkey Kong Barrel Blast was released for the Nintendo Wii. It was originally developed as a Gamecube game and would have used the bongo controller, but it was delayed and released exclusively as a Wii title with no support for the bongo accessory. Super Smash Bros. Brawl features music from the game arranged by Hirokazu "Hip" Tanaka[25] and a stage called "75m", an almost exact replica of its Donkey Kong namesake.[60] While the stage contains her items, Pauline is missing from her perch at the top of the stage.[60]
Its success entrenched the game in American popular culture. In 1982, Buckner and Garcia and R. Cade and the Video Victims both recorded songs based on the game. Artists like DJ Jazzy Jeff & the Fresh Prince and Trace Adkins referenced the game in songs. Episodes of television series such as The Simpsons, Futurama, Crank Yankers, and Fairly Odd Parents have also contained references to the game. Even today, sound effects from the Atari 2600 version often serve as generic video game sounds in films and television shows. The Killer List of Videogames ranks Donkey Kong the third most popular arcade game of all time and places it at #25 on the "Top 100 Videogames" list. in February 2006, Nintendo Power rated it the 148th best game made on a Nintendo System.[61] Today, Donkey Kong is the fifth most popular arcade game among collectors.[62] The 2007 motion picture documentary The King of Kong: A Fistful of Quarters explores the world of competitive classic arcade gaming and tells the story of Steve Wiebe's quest to beat Billy Mitchell's world high score in Donkey Kong.[63]
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 (2004) Album notes for Famicom 20th Anniversary Original Sound Tracks Vol. 1. Scitron Digital Contents Inc..
- ↑ Crawford 94.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 De Maria 82.
- ↑ Day (Twin Galaxies).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 The King of Kong.
- ↑ Sellers 66.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kohler 39.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ray 19–20.
- ↑ Kohler 37.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 De Maria 238.
- ↑ Kohler 40–42.
- ↑ Kent 157.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Kent 158.
- ↑ Company:Ikegami Tsushinki. Game Developer Research Institute. Retrieved on 2009-05-17.
- ↑ ドンキーコング裁判についてちょこっと考えてみる (Thinking a bit about Donkey Kong). Retrieved on 2009-02-01.
- ↑ It started from Pong (それは『ポン』から始まった : アーケードTVゲームの成り立ち sore wa pon kara hajimatta: ākēdo terebi gēmu no naritachi), Masumi Akagi (赤木真澄 Akagi Masumi), Amusement Tsūshinsha (アミューズメント通信社 Amyūzumento Tsūshinsha), 2005, ISBN 4-9902512-0-2.
- ↑ Both quotes from Sheff 47.
- ↑ Kohler 36.
- ↑ Kohler 38.
- ↑ Mikkelson and Mikkelson.
- ↑ Sheff 48–49.
- ↑ Sheff 47–48.
- ↑ Kohler 38–39.
- ↑ Kent 530.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Smash Bros. DOJO!!, Donkey Kong
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Kent 159.
- ↑ Sheff 49.
- ↑ Sheff 109.
- ↑ Kohler 212.
- ↑ Sellers 68.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Sheff 110.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Kent 211.
- ↑ Quoted in Kohler 5.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Kent 160.
- ↑ Sheff 113.
- ↑ Sheff 111.
- ↑ Kent 284.
- ↑ Kohler 46.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Kent 215.
- ↑ Quoted in Sheff 111.
- ↑ Kent 208–209.
- ↑ Sheff 112.
- ↑ Kent 210.
- ↑ Kent 283–285.
- ↑ Parish.
- ↑ Kent 210–211.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1984, 119.
- ↑ Sheff 121.
- ↑ Kent 214.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1986, 74–75.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1986, 74.
- ↑ Kent 217.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1984, 118.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1984, 112.
- ↑ Kent 218.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1986, 72.
- ↑ Second Court of Appeals, 1986, 77–78.
- ↑ Quoted in Sheff 126.
- ↑ Sheff 127.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 "Smash Bros. DOJO!! - 75m". Smash Bros.Dojo. http://www.smashbros.com/en_us/stages/stage30.html. Retrieved 2008-03-08.
- ↑ Michaud, Pete (February 2006). "NP Top 200". Nintendo Power 197: 58.
- ↑ McLemore.
- ↑ "The King of Kong: A Fistful of Quarters > Overview". Allmovie. http://allmovie.com/work/the-king-of-kong-a-fistful-of-quarters-384804. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
References
- Consalvo, Mia (2003). “Hot Dates and Fairy-tale Romances”. The Video Game Theory Reader. New York: Routledge.
- Crawford, Chris (2003). Chris Crawford on Game Design. New Riders Publishing.
- Day, Walter, chief ed. (2007). Donkey Kong: Points [Hammers Allowed] [Default, TGTS]". Twin Galaxies, LLC.
- De Maria, Rusel, and Wilson, Johnny L. (2004). High Score!: The Illustrated History of Electronic Games. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill/Osborne.
- Fox, Matt (2006). The Video Games Guide. Boxtree Ltd.
- Gordon, Seth, director (2007). The King of Kong: A Fistful of Quarters. Picturehouse.
- Kent, Steven L. (2001). The Ultimate History of Video Games: The Story behind the Craze that Touched Our Lives and Changed the World. New York City: Three Rivers Press.
- Kohler, Chris (2005). Power-up: How Japanese Video Games Gave the World an Extra Life. Indianapolis, Indiana: BradyGAMES.
- McLemore, Greg, et al. (2005). "The Top Coin-operated Videogames of All Time". Retrieved 15 February 2006.
- Mikkelson, Barbara, and Mikkelson, David (February 25, 2001). "Donkey Wrong." Snopes.com. Retrieved August 15, 2006.
- Mingo, Jack. (1994) How the Cadillac Got its Fins New York: HarperBusiness. ISBN 0-88730-677-2
- Miyamoto, Shigeru, designer (1981). Donkey Kong. Nintendo.
- Parish, Jeremy (2006-10-31). "Wii Virtual Console Lineup Unveiled". 1UP.com. http://www.1up.com/do/newsStory?cId=3154811. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
- Ray, Sheri Graner (2004). Gender Inclusive Game Design: Expanding the Market. Hingham, Massachusetts: Charles Rivers Media, Inc.
- Schodt, Frederick L. (1996). Dreamland Japan: Writings on Modern Manga. Berkeley, California: Stone Bridge Press.
- Sellers, John (2001). Arcade Fever: The Fan's Guide to the Golden Age of Video Games. Philadelphia: Running Book Publishers.
- Sheff, David (1999). Game Over: Press Start to Continue: The Maturing of Mario. Wilton, Connecticut: GamePress.
- United States Court of Appeals, Second Circuit (October 4, 1984). Universal City Studios, Inc. v. Nintendo Co., Ltd.
- United States Court of Appeals, Second Circuit (15 July 1986). Universal City Studios, Inc. v. Nintendo Co., Ltd.
External links
- Donkey Kong at the Killer List of Videogames
- Arcade-History.com entry for Donkey Kong
- Donkey Kong world records at Twin Galaxies Scoreboard
- Donkey Kong at MobyGames
- Donkey Kong guide at StrategyWiki
- Donkey Kong at NinDB
- A comparison and resource page of classical versions of Donkey Kong
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||